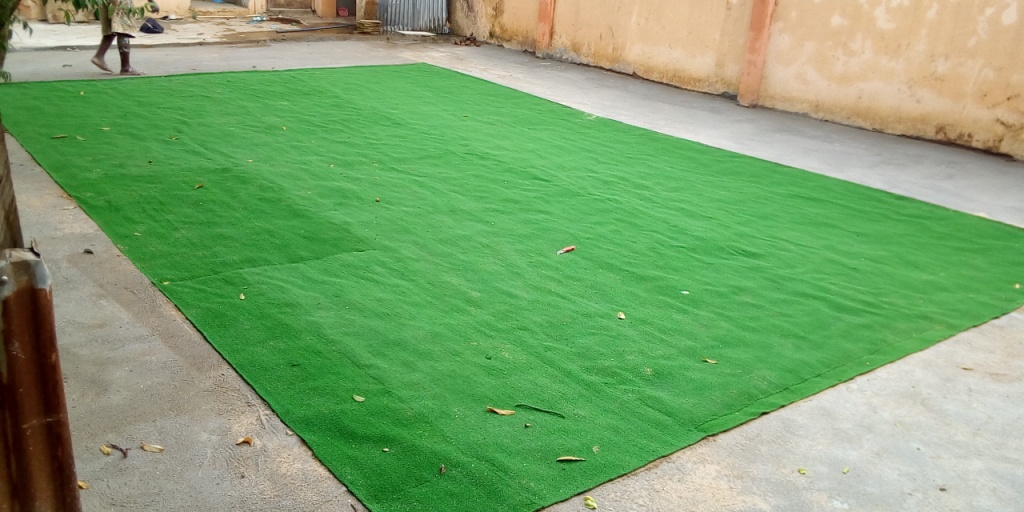
Artificial turf is a surface of synthetic fibers made to look like natural grass. It is most often used in arenas for sports that were originally or are normally played on grass. However, it is now being used on residential lawns and commercial applications as well. The main reason is maintenance—artificial turf stands up to heavy use, such as in sports, and requires no irrigation or trimming. Domed, covered, and partially covered stadiums may require artificial turf because of the difficulty of getting grass enough sunlight to stay healthy. Artificial turf does have its downside, however: limited life, periodic cleaning requirements, petroleum use, toxic chemicals from infill, and heightened health and safety concerns.

Artificial Grass First gained substantial attention 53 years ago in 1966, when it was installed in the year-old Astrodome. The specific product used was “ChemGrass”, developed by Monsanto and rebranded as AstroTurf; this term since then became a generic trademark for any artificial turf throughout the late 20th century. AstroTurf remains a registered trademark but is no longer owned by Monsanto.
The first generation turf systems (i.e., short-pile fibers without infill) of the 1960s have been largely replaced by the second generation and third generation turf systems. Second generation synthetic turf systems feature longer fibers and sand infills, and third generation systems, which are most widely used today, offer infills that are mixtures of sand and granules of recycled rubber, or “rubber crumb”.